Let’s learn yourself how to calculate moving sum and moving average using Numpy Convolve. We will get to know a few tricks of Numpy Convolve function.
The easiest moving sum
First let’s see how to calculate the most basic version of moving sum. Let’s have given list of numbers. To calculate moving sum use Numpy Convolve function taking list as an argument. The second one will be ones_like of list.
import numpy as np
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
moving_sum = np.convolve(my_list, np.ones_like(my_list))
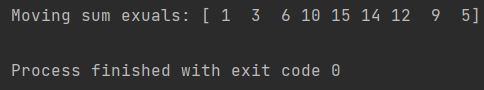
print(f"Moving sum exuals: {moving_sum}")

As you can see moving sum has been calculated. Here’s how it was calculated:
1
1 + 2 = 3
1 + 2 + 3 = 6
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 14
3 + 4 + 5 = 12
4 + 5 = 9
5
Convolve method
The are 3 different parameters of Convolve function. Let’s see how they work. Valid parameter goes as a first one.
import numpy as np
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
moving_sum = np.convolve(my_list, np.ones_like(my_list),'valid')
print(f"Moving valid sum exuals: {moving_sum}")
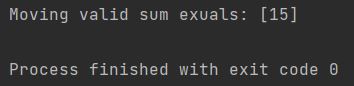
You can see that only the highest value has been returned.
And this is how the “Same” parameter works.
import numpy as np
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
moving_sum = np.convolve(my_list, np.ones_like(my_list),'same')
print(f"Moving same sum exuals: {moving_sum}")
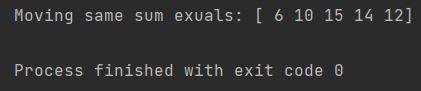
In our example “same” just skipped the lowest values.
“Full” we will see as the latest one.
import numpy as np
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
moving_sum = np.convolve(my_list, np.ones_like(my_list),'full')
print(f"Moving full sum exuals: {moving_sum}")
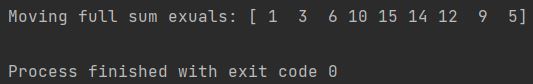
As you see the result is the same as for regular Convolve. This is because “full” is a default option.
We already know how to calculate moving sum. Then we are ready to calculate moving mean in Python.
To calculate moving average you first need to create a denominator. You can do it thanks to list comprehension.
To calculate the moving mean just divide moving average by your denominator like that:
import numpy as np
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
denominator = list(range(1, 5)) + list(range(5, 0, -1))
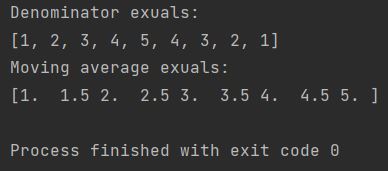
print(f"Denominator exuals: \n{denominator}")
moving_average = np.convolve(my_list, np.ones_like(my_list)) / denominator
print(f"Moving average exuals: \n{moving_average}")

Here is my short explanation on how moving average has been calculated exactly:
1 / 1 = 1
(1 + 2) / 2 = 1.5
( 1 + 2 + 3) / 3 = 2
(1 + 2 + 3 + 4) / 4 = 2.5
(1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5) / 5 = 3
(2 + 3 + 4 + 5) / 4 = 3.5
(3 + 4 + 5) / 3 = 4
(4 + 5) / 2 = 4.5
5 / 1 = 5
