Learn how to rank values in NumPy arrays using the argsort() function to sort by rows or columns with axis parameters.
When analyzing arrays, you often need to know the ranking or ordering of values rather than the values themselves for sorting and indexing operations.
How to Rank Array Values Using NumPy’s argsort() Function by Axis
See how to rank values using the argsort Numpy function.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[1, 56, 55, 15],
[5, 4, 33, 53],
[3, 6, 7, 19]])
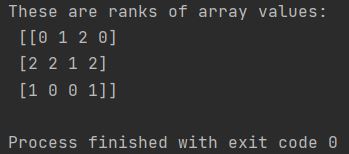
sorted_array = np.argsort(my_array, axis=0)
print(f"These are ranks of array values: \n {sorted_array}")

As you can see, there are ranks given for the values in your array. You can work on them further.
How to Rank Array Values Along Rows Using axis=1 Parameter
Do you want to rank it differently? No problem. See:
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[1, 56, 55, 15],
[5, 4, 33, 53],
[3, 6, 7, 19]])
sorted_array = np.argsort(my_array, axis=1)
print(f"These are ranks of array values: \n {sorted_array}")
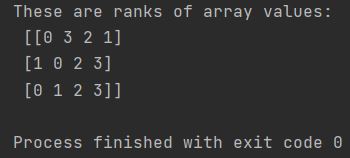
By changing the axis parameter to 1, the ranking is performed within each row rather than each column.
The np.argsort() function returns integer indices, not sorted values. Use these indices with array indexing to access sorted elements or combine with other functions for advanced sorting operations.
