This guide shows how to calculate correlation between arrays in NumPy using np.corrcoef(), which returns the Pearson correlation coefficient matrix for two or more arrays.
How to Calculate Correlation Between Arrays in Numpy
NumPy’s np.corrcoef(array1, array2) computes the full correlation matrix where the off-diagonal element gives the Pearson correlation coefficient between the two input arrays.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([1, 2, 4, 7, 17, 43, 4, 9])
second_array = np.array([2, 12, 5, 43, 5, 76, 23, 12])
correlation_arrays = np.corrcoef(my_array, second_array)
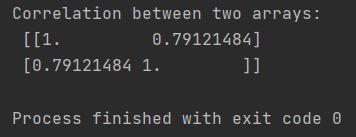
print(f"Correlation between two arrays: \n {correlation_arrays}")
The corrcoef function computes the correlation matrix, providing you with valuable insights into the relationship between the two arrays.
Interpreting Array Correlation
Understanding the correlation coefficient output by Numpy’s corrcoef function is essential to interpret the relationship between two arrays.
Correlation Coefficient
The correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to 1.
A positive value (close to 1) indicates a strong positive correlation, meaning the arrays move in the same direction.
A negative value (close to -1) signifies a strong negative correlation, indicating opposite movements.
A value close to 0 implies a weak or no linear correlation between the arrays.
Here’s a simple code snippet to interpret the correlation coefficient:
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([1, 2, 4, 7, 17, 43, 4, 9])
second_array = np.array([2, 12, 5, 43, 5, 76, 23, 12])
correlation_arrays = np.corrcoef(my_array, second_array)
correlation_coefficient = correlation_arrays[0, 1]
if correlation_coefficient > 0:
print("There is a positive correlation between the arrays.")
elif correlation_coefficient < 0:
print("There is a negative correlation between the arrays.")
else:
print("There is no significant linear correlation between the arrays.")
By analyzing the correlation coefficient, you can gain valuable insights into the relationship and dependencies between your arrays.
