The harmonic mean is a type of average useful for rates and ratios, and this guide shows how to calculate harmonic mean in Python using the built-in statistics module, SciPy, or manual formulas. Let’s see how to calculate harmonic mean in Python.
To calculate the harmonic mean, we need to import the statistics module.
Using the statistics Module
Python’s statistics.harmonic_mean() function makes it simple to calculate harmonic mean in Python from a list of numbers, automatically handling the reciprocal sum formula for you.
import statistics as s
x = [1, 5, 7, 8, 43, 6]
harmonic_mean = s.harmonic_mean(x)
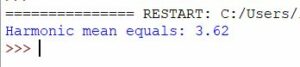
print(f"Harmonic mean equals: {round(harmonic_mean, 2)}")
This function automatically handles the calculation, making it a convenient option.
Using scipy.stats.hmean
For those working in scientific computing, the scipy library offers an alternative:
from scipy.stats import hmean
x = [1, 5, 7, 8, 43, 6]
harmonic_mean = hmean(x)
print(f"Harmonic mean equals: {round(harmonic_mean, 2)}")
Manual Calculation
Alternatively, you can perform the harmonic mean calculation manually to gain insight into how it works:
x = [1, 5, 7, 8, 43, 6]
harmonic_mean = len(x) / sum(1 / item for item in x)
print(f"Harmonic mean equals: {round(harmonic_mean, 2)}")
