Let’s learn how to calculate exponential value in Python using the exponentiation operator **, the built‑in pow() function, and math module helpers like math.pow() and math.exp(). This knowledge can be valuable in various scientific, engineering, and mathematical applications.
In mathematics, exponentiation is the operation of raising a base number to a certain power (the exponent). Python provides several ways to compute exponential values, catering to different needs and levels of precision.
Using the Exponentiation Operator
For most use cases, the easiest way to calculate exponential value in Python is with the ** operator for powers of any base, and math.exp() when you specifically need the natural exponential function ex.
my_base = 5
my_exponent = 3
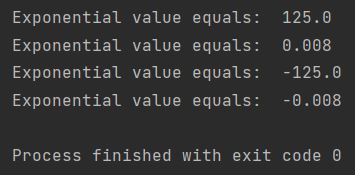
print ("Exponential value equals: ", my_base ** my_exponent)
my_base = 5
my_exponent = -3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", my_base ** my_exponent)
my_base = -5
my_exponent = 3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", my_base ** my_exponent)
my_base = -5
my_exponent = -3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", my_base ** my_exponent)

The exponentiation operator ** is a built-in Python operator, offering a concise and readable way to calculate powers.
Using a pow method
Alternatively, you can use the pow function from the math module.
Another approach is to employ the pow() function available within the math module.
import math
my_base = 5
my_exponent = 3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", math.pow(my_base, my_exponent))
my_base = 5
my_exponent = -3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", math.pow(my_base, my_exponent))
my_base = -5
my_exponent = 3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", math.pow(my_base, my_exponent))
my_base = -5
my_exponent = -3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", math.pow(my_base, my_exponent))

You can also perform modular exponentiation using the three-argument pow(base, exponent, modulo) form, if needed for more advanced mathematical operations.
Using an exp method
In case you would like to calculate the exponential value of Euler’s constant number you need to use exp method of math module.
import math
my_exponent = 3
print ("Exponential value equals: ", math.exp(my_exponent))
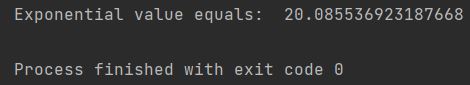
The math.exp(x) function is specifically designed to calculate the exponential function, ex, where e is Euler’s number (approximately 2.71828…).
