Learn how to convert NumPy arrays to XYZ file format for molecular modeling, crystallography, and scientific data representation.
This knowledge enhances your data handling capabilities and makes it easier to work with a variety of data formats.
Having a file means you can format it as a Numpy array using existing functions.
The XYZ file format stores 3D atomic coordinates: line 1 = atom count, line 2 = comment, lines 3+ = element symbol + x, y, z coordinates (space-separated).
Structuring NumPy Arrays for XYZ Format
By using the reshape method with -1 as a parameter, you can efficiently structure your data into the required format, which can be particularly useful in scientific or engineering fields where XYZ files are commonly used for representing three-dimensional spatial data.
Before converting to XYZ, it’s often necessary to load data from a text file or another source into a NumPy array. The following code snippet demonstrates how to load data from a text file named veryimportantfile.txt (you should replace this with your actual file path) using np.genfromtxt. Crucially, ensure that veryimportantfile.txt is formatted such that each line contains data suitable for XYZ conversion – typically, each line should represent an atom and its x, y, and z coordinates, separated by spaces or commas. For this example, we assume the file contains space-separated values.
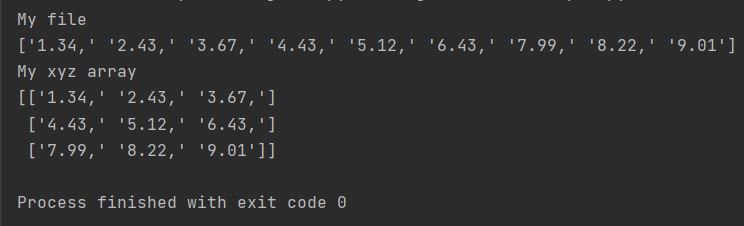
import numpy as np
my_file = np.genfromtxt('C:/Users/Pythoneo/Documents/veryimportantfile.txt', dtype='str')
print(f"My file \n{my_file}")
my_array = np.array(my_file)
my_array = my_array.reshape(-1, 3)
print(f"My xyz array \n{my_array}")

reshape(-1, 3) automatically structures data into 3-column format; -1 infers row count from total elements, useful for XYZ’s (element, x, y, z) structure.
Using reshape(-1, 3) automates formatting, making it ideal for workflows involving scientific or engineering datasets.
Writing the XYZ File
Once your data is structured correctly, writing it to an XYZ file involves iterating over the array and formatting each line correctly. Each line will typically consist of an element symbol followed by its coordinates.
with open('output.xyz', 'w') as file:
for row in my_array:
line = ' '.join(map(str, row)) # Convert each element to string and join
file.write(line + '\n')
This script assumes that your Numpy array contains the correct atomic symbols and coordinates. Make sure your data is accurate and correctly formatted before converting it to the XYZ format.
This skill is particularly useful in fields like computational chemistry, physics, and materials science, where XYZ files are commonly used to represent molecular and crystal structures.
