NumPy is a Python library for scientific computing. It provides a number of functions for working with arrays, including the ability to flatten an array.
Let’s check how to flatten an array in Numpy Python library.
You can flatten your multidimensional array with NumPy. There are even two ways to do that.
How to flatten an array using Numpy flatten function?
The flatten() method converts multidimensional arrays into 1D arrays, returning a new independent copy of the data. See below example.
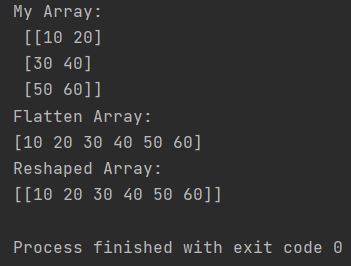
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]).reshape(3, -1)
print("My Array: \n", my_array)
flatten_array = my_array.flatten()
print(f"Flatten Array: \n{flatten_array}")
The NumPy flatten method flattens the array. The flatten function just change multi dimension array into 1d array. In this example I showed how to change 2d array into 1d array.
How to flatten an array using Numpy reshape function?
Using reshape(-1,) or reshape(array.size) creates a 1D view of the data; reshape(1, -1) creates a 2D array (1 row), not a true 1D array.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]).reshape(1, -1)
print("My Array: \n", my_array)
reshaped_array = my_array.reshape(1, -1)
print(f"Reshaped Array: \n{reshaped_array}")
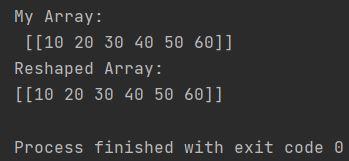
As you can see array got flattened as well.
How to flatten an array using Numpy ravel function?
The ravel() method returns a flattened 1D view (reference) of the array; changes affect the original array if it’s C-contiguous. flatten() creates independent copy; ravel() returns view when possible—ravel() is faster for memory, flatten() is safer for modifications.
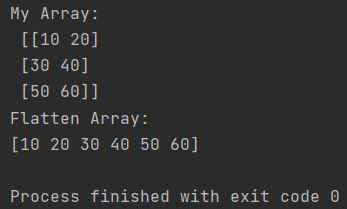
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]).reshape(3, -1)
print("My Array: \n", my_array)
flatten_array = my_array.ravel()
print(f"Flatten Array: \n{flatten_array}")
Outputs match but methods differ: ravel() is faster (returns view), flatten() is safer (returns copy), reshape() can create different shapes.
Flatten Array: [10 20 30 40 50 60]
