Understanding how to calculate cumulative sums is essential in various data analysis and statistics tasks. Whether you’re tracking the running total of values over time or need to create cumulative sum columns or rows in a dataset, the Numpy cumsum method provides a convenient and efficient way to achieve this.
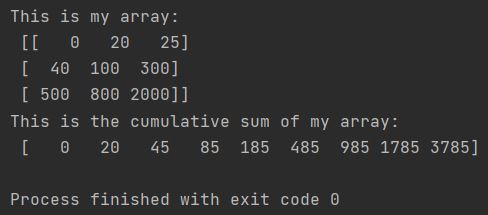
To calculate a cumulative sum in Python, you need to use the cumsum method from the NumPy library. Your array is the parameter which needs to be used. I created sample 3 x 3 array which I will sum up cumulatively.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([0, 20, 25, 40, 100, 300,
500, 800, 2000]).reshape(3, -1)
print(f"This is my array: \n {my_array}")
my_cumsum_array = np.cumsum(my_array)
print(f"This is the cumulative sum of my array"
f":\n {my_cumsum_array}")

As you can see Python summed every element up.
How to create a cumulative sum column in python?
It is also possible to calculate a cumulative sum column-wise by specifying an axis parameter in the cumsum method. You need to add axis parameters to cumsum method.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([0, 20, 25, 40, 100, 300,
500, 800, 2000]).reshape(3, -1)
print(f"This is my array: \n {my_array}")
my_cumsum_array = np.cumsum(my_array, axis=0)
print(f"This is the cumulative columns sum of my array"
f":\n {my_cumsum_array}")
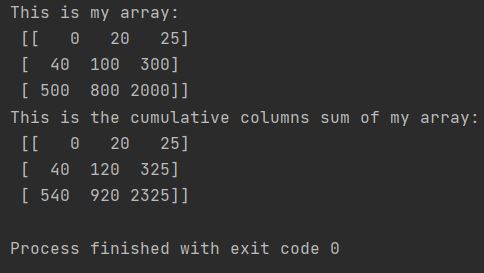
With axis=0, result shape matches input; each element is the cumulative sum of all elements above it in the same column.
How to create a cumulative sum row in python?
Now, observe the difference when we change the axis value to 1 for row-wise cumulative sum calculation. This is how to calculate cum sum for a row.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([0, 20, 25, 40, 100, 300,
500, 800, 2000]).reshape(3, -1)
print(f"This is my array: \n {my_array}")
my_cumsum_array = np.cumsum(my_array, axis=1)
print(f"This is the cumulative rows sum of my array"
f":\n {my_cumsum_array}")
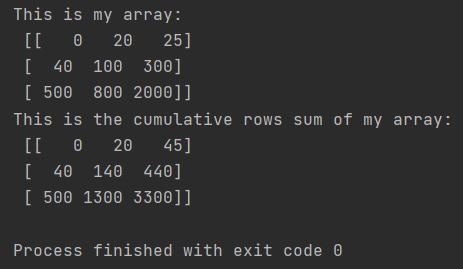
With axis=1, result shape matches input; each element is the cumulative sum of all elements to its left in the same row.
