Following is the help on how to enumerate dictionary in Python. Enumerate dictionary in Python using enumerate() with .items() lets you iterate through key-value pairs while tracking each pair’s insertion order index, perfect for numbered lists or ordered processing.
Consider the following Python dictionary as an example:
my_dictionary = {'Audi' : 1000, 'BMW' : 2000, 'Mercedes' : 3000}
It’s important to note that while .items() provides key-value pairs, the order in which these pairs are presented was arbitrary in Python versions prior to 3.7. In Python 3.7 and later, dictionaries maintain insertion order, so enumeration will reflect the order in which items were originally added to the dictionary.
Step-by-Step Dictionary Enumeration in Python
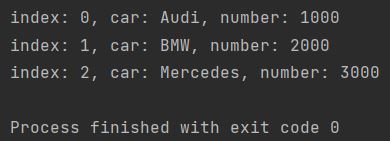
The following code shows how to enumerate dictionary in Python using enumerate(my_dictionary.items()), unpacking each (index, (key, value)) tuple for complete access during iteration.
my_dictionary = {'Audi' : 1000, 'BMW' : 2000, 'Mercedes' : 3000}
for i, (car, number) in enumerate(my_dictionary.items()):
print("index: {}, car: {}, number: {}".format(i, car, number))
In the provided code snippet, the enumerate() function is employed to generate an index (i) for each iteration and simultaneously unpack the key-value pairs (assigned to variables car and number) obtained from my_dictionary.items(). We then print the index, car brand, and the corresponding number for each item in the dictionary.

By enumerating the dictionary, you can efficiently access and process its key-value pairs, making it a valuable tool for various data manipulation and analysis tasks in Python.
