This Python guide introduces you to calculating the absolute value using Numpy, along with several practical techniques.
How to Calculate Absolute Values with Numpy
NumPy’s np.abs() provides the simplest way to calculate absolute value using NumPy for scalars, arrays, matrices, and even complex numbers (returning magnitude).
import numpy as np
my_scalar = -77
my_abs_value = np.abs(my_scalar)
print(f"My absolute value equals: {my_abs_value}")
For example, the absolute value of the scalar value -77 is 77.
You can also calculate the absolute values of arrays in a similar manner:
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([-1, -2])
my_abs_value = np.abs(my_array)
print(f"My absolute value equals: {my_abs_value}")
For instance, applying np.abs() to a NumPy array containing the elements -1 and -2 yields a new array with the absolute values [1, 2].
Regardless of the array’s size, the calculation remains the same:
import numpy as np
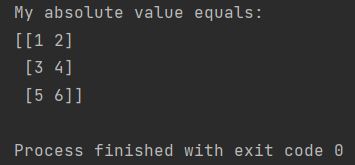
my_array = np.array([[-1, -2], [3, -4], [-5, 6]])
my_abs_value = np.abs(my_array)
print(f"My absolute value equals: \n{my_abs_value}")

Calculating Absolute Differences in Numpy Matrices
You can also compute the absolute difference between Numpy matrices:
import numpy as np
my_first_array = [[-2, -3, 4], [-4, 5, -6]]
my_second_array = [[-1, 2, 7], [-8, 9, -9]]
my_first_array, my_second_array = map(np.array, (my_first_array, my_second_array))
abs_difference = np.abs(my_first_array) - np.abs(my_second_array)
print(f"The absolute difference between arrays equals: \n{abs_difference}")
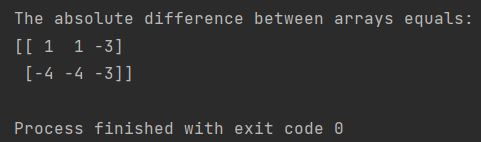
In this demonstration, we have applied np.abs() separately to two arrays and then computed the element-wise difference of these absolute value arrays. NumPy’s vectorized operations enable a wide range of mathematical computations on arrays and matrices in an analogous manner.
Numpy Functions for Absolute Value
Both np.abs() and np.absolute() work identically to calculate absolute value using NumPy np.abs, with the shorter np.abs() being the conventional choice for element-wise absolute operations.
