Let’s learn how to generate evenly spaced samples in NumPy using np.linspace(), which creates arrays with a specified number of points between start and stop values. We will use Numpy linspace method for that purpose.
To generate evenly spaced sample within given interval you may need linpsace function. It generates the array and takes starting point, end point and the number of needed elements.
How to Use Numpy Linspace Method for Evenly Spaced Arrays
np.linspace(start, stop, num) generates evenly spaced samples in NumPy across the interval, including the endpoint by default and supporting customization via endpoint, dtype, and retstep parameters. It takes starting point, end point and the number of needed elements as its parameters.
The syntax for the linspace method is as follows:
linspace(start, end, num=5)
Where:
start is the starting point of the interval end is the end point of the interval num is the number of elements to be generated
The simpliest example
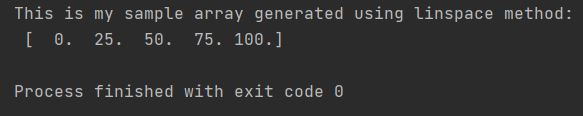
Let’s see how to generate even sample from 0 to 100. I will need 5 elements in my sample array.
import numpy as np
cities = ["New York", "London", "Austin", "Chicago", "Quebec"]
my_linspace_array = np.linspace(0, 100, len(cities))
print(f"This is my sample array generated using linspace method: "
f"\n {my_linspace_array}")
In this example, the num parameter is set to len(cities), which is 5. This instructs numpy.linspace to generate exactly 5 evenly spaced numbers between 0 and 100 (inclusive by default). The spacing between consecutive numbers in the resulting array is automatically calculated by linspace to ensure that the range from the start point to the end point is divided into num - 1 equal intervals. Therefore, the spacing is (end - start) / (num - 1), or in this case, (100 - 0) / (5 - 1) = 25.
More advanced example
You can even add more parameters to your code:
import numpy as np
my_array = ([0, 20, 25, 40, 100])
my_linspace_array = np.linspace(min(my_array), max(my_array), len(my_array))
print(f"This is my sample array generated using linspace method: "
f"\n {my_linspace_array}")
The result is the same. Linspace interval is fully parametrized by my_array list.
It’s important to reiterate that while this example uses len(my_array) for the num parameter, and the range is determined by the minimum and maximum values *within* my_array, the resulting my_linspace_array will not be identical to my_array. Instead, it will be a new array containing evenly spaced values spanning the numerical range of my_array. This is a common pattern when you want to create a smooth, evenly spaced representation of the data’s range, even if the original data points are not evenly spaced themselves.
Other parameters of Numpy linspace method
The linspace method in Numpy has several other parameters that can be used to customize the output.
-
endpoint : If set to True, the end point will be included in the output array. The default value is True.
dtype : The data type of the output array. The default value is float.
retstep : If set to True, the step size between elements in the output array will be returned as well. The default value is False.
For example, the following code will generate 10 evenly spaced sample from 0 to 100, but the end point will not be included in the output array:
import numpy as np
my_linspace_array = np.linspace(0, 100, 10, endpoint=False)
print(f"This is my sample array generated using linspace method: "
f"\n {my_linspace_array}")
Both linspace and arange are essential tools in NumPy for creating numerical sequences.
