Learn how to compute matrix inverses in Python using NumPy’s linalg.inv() function with practical examples and error handling techniques.
How to Invert a Matrix in NumPy Using linalg.inv() Function
The Numpy function ‘linalg.inv()’ can be used to inverse a matrix. The syntax for the ‘linalg.inv()’ function is:
np.linalg.inv(matrix)
Where ‘matrix’ is the matrix that you want to inverse.
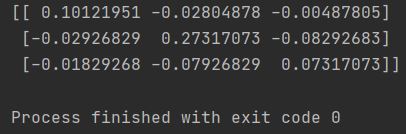
For example, the following code inverses the matrix ‘my_array’:
import numpy as np my_array = np.array([[11, 2, 3], [3, 6, 7], [6, 7, 22]]) inverted_array = np.linalg.inv(my_array) print(my_array) print(inverted_array)
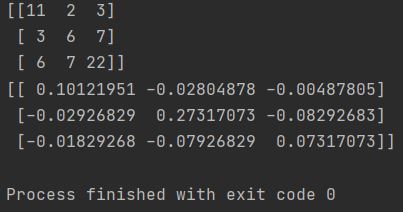
The output of the linalg.inv() function is the inverse of the matrix.
How to Check Matrix Invertibility Using Determinants and Error Handling in NumPy
There are a few ways to check if a matrix is invertible. One way is to use the linalg.inv() function. If the linalg.inv() function returns an error, then the matrix is not invertible.
Another way to check if a matrix is invertible is to use the determinant of the matrix. The determinant of a matrix is a number that tells you whether the matrix is invertible or not. If the determinant of the matrix is equal to 0, then the matrix is not invertible.
Here is an example of how to check if a matrix is invertible using the determinant:
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[11, 2, 3], [3, 6, 7], [6, 7, 22]])
determinant = np.linalg.det(my_array)
if determinant == 0:
print("The matrix is not invertible.")
else:
print("The matrix is invertible.")
In this example, the determinant of the matrix is not equal to 0, so the matrix is invertible.
To learn more about the linalg.inv() function, please refer to the Numpy documentation
