Learn how to remove outliers and trim array values using NumPy’s clip() function to constrain values within specified bounds.
Suppose we have an array:
[0.006, 2, 5, 8, 10, 25, 400]
Clipping an array
We would like to exclude extremum values. Numpy clip function allows us to exclude very low and high values.
Use np.clip() to cap values below 2 to 2 and values above 25 to 25, effectively removing outliers while preserving array structure.
import numpy as np
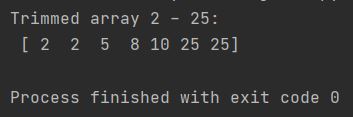
my_array = np.array([0, 2, 5, 8, 10, 25, 40])
trim_array = np.clip(my_array, 2, 25)
print(f"Trimmed array 2 - 25: \n {trim_array}")
As you may noticed the syntax of clip function is as follows: clip(my_array, min_value, max_value).
How to Use None Parameters for Flexible Clipping Bounds in np.clip()
It’s not necessary to specify both minimum and maximum values for clipping. You can use the None parameter to leave one of these bounds unchanged.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([0, 2, 5, 8, 10, 25, 40])
trim_array = np.clip(my_array, None, 25)
print(f"My array: \n {my_array}")
print(f"Trimmed array < 25: \n {trim_array}")
The output would be:
My array: [ 0 2 5 8 10 25 40] Trimmed array < 25: [ 0 2 5 8 10 25 25]
You can also use predefined constants as parameters for the clip function to specify the clipping bounds.
import numpy as np
min_value = 1
my_array = np.array([0, 2, 5, 8, 10, 25, 40])
trim_array = np.clip(my_array, min_value, None)
print(f"My array: \n {my_array}")
print(f"Trimmed array > min_value: \n {trim_array}")
Here's an output where values are trimmed between min_value and max value is not defined.
My array: [ 0 2 5 8 10 25 40] Trimmed array > min_value: [ 1 2 5 8 10 25 40]
As you can notice the values are trimmed. 0 is replaced by 1 and 40 is still present.
NumPy's clip() function is an efficient method for outlier removal, data normalization, and constraining values within acceptable ranges for statistical analysis and machine learning preprocessing.
