Learn how to create 3D meshgrid arrays in NumPy using np.meshgrid() to generate coordinate grids for multidimensional data processing and visualization.
Generating Three Arrays
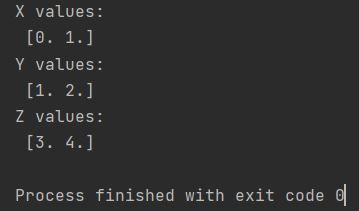
Create three 1D arrays representing coordinate values along x, y, and z axes using np.linspace() for evenly-spaced values.
import numpy as np
xs = np.linspace(0., 1., 2)
ys = np.linspace(1., 2., 2)
zs = np.linspace(3., 4., 2)
print(f"X values: \n {xs}")
print(f"Y values: \n {ys}")
print(f"Z values: \n {zs}")
The resulting arrays contain evenly spaced values: xs=[0., 1.], ys=[1., 2.], zs=[3., 4.].
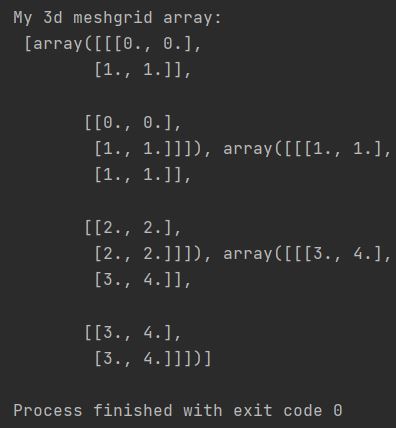
Generating a 3D Meshgrid Array
Use np.meshgrid(xs, ys, zs) to create three 3D coordinate arrays containing all combinations of input values.
import numpy as np
xs = np.linspace(0., 1., 2)
ys = np.linspace(1., 2., 2)
zs = np.linspace(3., 4., 2)
meshgrid_array = np.meshgrid(xs, ys, zs)
print(f"My 3d meshgrid array: \n {meshgrid_array}")
meshgrid() returns a tuple of three 3D arrays where each element [i,j,k] contains coordinate values for that position in 3D space.
Here is what a 3D meshgrid array looks like:

Other Ways to Generate a 3D Meshgrid Array
Alternative approaches: use np.ix_() for advanced indexing, or itertools.product() for Cartesian products; np.meshgrid() is optimized for regular grids.
You can learn more about meshgrid arrays in Numpy by reading the Numpy documentation.
