Learn how to stack arrays in NumPy using vstack(), hstack(), stack(), and dstack() functions to combine and reshape multi-dimensional data for efficient data manipulation.
Arrays are stackable. I’ll show how to stack array vertically and horizontally in Python Numpy.
How to Stack Arrays Vertically Using NumPy’s vstack() Function
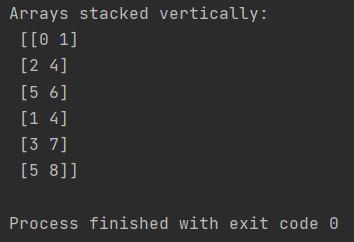
To stack arrays vertically use Numpy vstack function.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 4], [5, 6]])
my_second_array = np.array([[1, 4], [3, 7], [5, 8]])
stacked_array = np.vstack((my_array, my_second_array))
print(f"Arrays stacked vertically: \n {stacked_array}")

How to Stack Arrays Horizontally Using NumPy’s hstack() Function
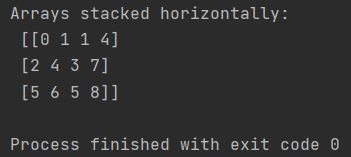
Similarlly you can stack array horizontally with Numpy hstack function.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 4], [5, 6]])
my_second_array = np.array([[1, 4], [3, 7], [5, 8]])
stacked_array = np.hstack((my_array, my_second_array))
print(f"Arrays stacked horizontally: \n {stacked_array}")
How to Stack Arrays Using Different Axes with NumPy’s stack() Function
Use NumPy’s np.stack() function with the axis parameter to stack arrays along specific dimensions, creating new axes and enabling multi-dimensional array construction.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 4], [5, 6]])
my_second_array = np.array([[1, 4], [3, 7], [5, 8]])
stacked_array = np.stack((my_array, my_second_array), axis=-1)
print(f"Arrays stacked using axis=-1: \n {stacked_array}")
stacked_array = np.stack((my_array, my_second_array), axis=1)
print(f"Arrays stacked using axis=1: \n {stacked_array}")
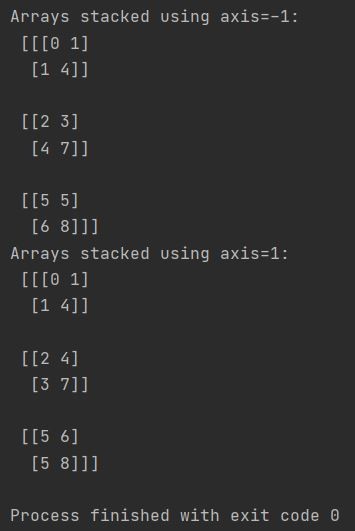
As you can see there are difference in outputs depends on axis parameter chosen.
For 3-dimension axes you can set axis parameter between -3 and 3 (including 0). For every other value you will get different outputs.
How to Stack Arrays Along the Third Axis Using NumPy’s dstack() Function
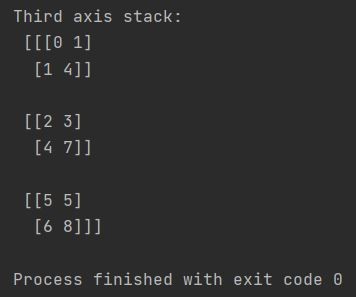
The other stacking possibility is also third axis stack. There is Numpy dstack function for that.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 4], [5, 6]])
my_second_array = np.array([[1, 4], [3, 7], [5, 8]])
stacked_array = np.dstack((my_array, my_second_array))
print(f"Third axis stack: \n {stacked_array}")
NumPy provides four primary array stacking methods (vstack, hstack, stack, dstack) for combining arrays along different axes and dimensions.
By mastering these techniques, you can efficiently stack arrays in NumPy for various data manipulation tasks, making your data processing more flexible and versatile.
